Reviewed by Tamir Rubin, Head of Product at iPREP • Updated February 2026
DANB CDA Sample Question
What is the purpose of a dental matrix?
- To cover the tooth and protect it from damage during a procedure.
- To create an impression of the tooth for a crown or bridge.
- To hold composite material in place while it is being cured.
- To remove calculus and plaque from the tooth surface.
General Chairside Assisting (GC)
95 questions • 75 minutes
- Patient assessment and chairside evaluation
- Communication and patient management basics
- Chairside procedures and instrument transfer
- Dental materials handling and properties
Radiation Health and Safety (RHS)
75 questions • 60 minutes
- Radiographic techniques and image quality
- Exposure settings, receptors, positioning basics
- Radiation biology, protection, regulations principles
- Infection prevention during radiography steps
Infection Control (ICE)
75 questions • 60 minutes
- Disease transmission routes and prevention
- Standard precautions and PPE use
- Instrument cleaning, packaging, sterilization cycles
- Disinfection, surface barriers, waste handling
- OSHA-style workplace safety protocols overview
Test Duration
Total time: 195 minutes (3 hours 15 min)
Timing is per component: GC 75 minutes, RHS 60 minutes, and ICE 60 minutes. Components may be scheduled separately or taken together, depending on your testing arrangement.
Test Breakdown & Sample Questions
Dental assisting certification helps candidates demonstrate job-ready knowledge and skills, and many employers recognize certification as a professional credential. The Dental Assisting National Board (DANB) offers multiple certification exams (including CDA, COA, and CPFDA); eligibility requirements vary by exam and may include a combination of education, work experience, and current CPR certification.
Certified Dental Assistant Exam Format
The CDA credential is earned by passing three component exams: General Chairside (GC), Radiation Health and Safety (RHS), and Infection Control (ICE).
| Component exam | Questions & time | Content areas |
|---|---|---|
| General Chairside (GC) | 95 questions · 75 minutes | Evaluation (17%); Patient Management (17%); Chairside Dentistry (50%); Dental Materials (16%) |
| Radiation Health and Safety (RHS) | 75 questions · 60 minutes | Radiographic procedures; Radiation safety; Infection prevention practices related to radiography |
| Infection Control (ICE) | 75 questions · 60 minutes | Disease transmission prevention; Cross-contamination prevention; Instrument/device processing; Workplace safety protocols |
The CDA exam consists of these three component exams taken as part of the CDA certification process.
General Chairside Assisting (GC)
The General Chairside (GC) exam evaluates chairside dental assisting knowledge and skills, including patient assessment and support, patient management, chairside procedures, and dental materials. The GC exam consists of 95 multiple-choice questions and has a testing time of 75 minutes.
GC Sample Question
What is the purpose of an air-water syringe in dental procedures?
- To remove excess tooth material
- To deliver a stream of air to dry the tooth surface
- To deliver a stream of water to clean the tooth surface
- To deliver a combination of air and water for rinsing and drying the tooth surface
The correct answer is D.
Explanation:
The air-water syringe is a commonly used dental instrument that delivers a combination of air and water for rinsing and drying the tooth surface during dental procedures. It is an important tool for maintaining a dry field, which is necessary for proper bonding, impression-making, and other dental procedures.
Radiation Health and Safety (RHS)
The Radiation Health and Safety (RHS) exam assesses knowledge and judgment related to dental radiography, including radiographic procedures, radiation safety, and infection prevention practices used during imaging. The RHS exam consists of 75 multiple-choice questions and has a testing time of 60 minutes.
RHS Sample Question
What is the purpose of a lead apron during dental radiography?
- To protect the patient from radiation exposure
- To protect the dental assistant from radiation exposure
- To protect the dental equipment from radiation damage
- To improve the quality of the dental radiographs
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
The lead apron is a protective barrier used during dental radiography to protect the patient from unnecessary radiation exposure. The lead apron is designed to absorb most of the scattered radiation that would otherwise reach the patient’s body. It is vital to use the lead apron during dental radiography to ensure patient safety and minimize radiation exposure.
Infection Control (ICE)
The Infection Control (ICE) exam evaluates knowledge and decision-making related to infection prevention in the dental setting, including preventing disease transmission and cross-contamination, processing instruments and devices, and workplace safety practices (including OSHA-related protocols). The ICE exam consists of 75 multiple-choice questions and has a testing time of 60 minutes.
ICE Sample Question
Which of the following is the most effective method for sterilizing dental instruments?
- Cold sterilization with glutaraldehyde
- Hot air sterilization
- Steam autoclaving
- Chemical disinfection with bleach
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
Steam autoclaving is the most effective method for sterilizing dental instruments. This method uses high temperature and pressure to kill all microorganisms on the surface of the instruments. Hot air sterilization and chemical disinfection with bleach are less effective and may not completely sterilize the tools.
Did you know?
The DANB CDA Exam has three sections: (1) General Chairside (GC), (2) Radiation Health and Safety (RHS), and (3) Infection Control (ICE). The CDA exam consists of 245 questions to be answered in 3 hours and 15 minutes. Scores range from 100 to 900, with a passing score of 400.
DANB CDA Preparation Strategy
Dental assisting can be a strong career path with steady demand, but the exact job outlook and workforce numbers change over time. To earn the CDA credential, you’ll need to pass all three CDA component exams, so a focused study plan matters.
Know your study style
Start with the approach that helps you learn fastest—visual notes and diagrams, audio lessons, or talking through concepts with a partner or group. If one method isn’t sticking, switch early instead of forcing it.
Treat study time like a job
Set a realistic schedule and protect it. Short, consistent sessions usually beat long, occasional ones. Use small time windows—lunch breaks, waiting rooms, commutes (audio only)—to review key facts and missed questions.
Take planned breaks
Studying too long without rest can backfire. Build in short breaks, and use a timer so breaks don’t turn into lost time.
Use an online prep course if it helps
A structured course can keep you on track and provide timed practice that matches the exam experience. Prioritize resources that include explanations, not just answers.
Invest in the right resources
Choose materials that match how you learn—question banks, flashcards, review guides, or video lessons. Start with one primary resource and add only what you’ll actually use.
Practice questions every week
Practice tests and targeted question sets help you learn the exam style and expose weak areas. Review every missed question and track patterns so you know what to fix next.
Believe in yourself
Confidence comes from preparation. Keep your plan simple, stay consistent, and walk into exam day knowing you’ve put in the work.
DANB CDA Exam Tips
Here are practical tips that can help you prepare for the CDA exams:
- Understand the exam content: Use the official outlines for GC, RHS, and ICE to guide what you study, and make sure you can apply concepts (not just memorize terms).
- Use quality study materials: Combine a content review resource with practice questions that include clear explanations.
- Create a study plan: Set a weekly schedule that rotates through GC, RHS, and ICE and includes regular review of missed questions.
- Practice time management: Take timed practice sets so pacing feels natural on exam day.
- Use support resources: Study with a partner or group, take a review course if needed, and ask a dental professional to clarify real-world procedures.
- Prepare the day before: Sleep well, gather what you need for check-in, and avoid cramming late at night.
- Stay calm and focused: Read each question carefully, eliminate weak options, and keep moving—mark tough questions and return if time allows.
DANB CDA Features
Become a Professional Dental Assistant
Earning the DANB Certified Dental Assistant (CDA) credential can strengthen your resume and help demonstrate that you meet a recognized standard of knowledge and skills for chairside dental assisting, radiography safety, and infection control.
Benefits of becoming certified
Many dental assistants pursue certification for reasons such as:
- Pride: Certification is a meaningful milestone that reflects your commitment to the profession.
- Confidence: Preparing for and passing an exam-based credential can help you feel more prepared for day-to-day responsibilities and patient-facing work.
- Commitment: Certification signals that you take professional standards seriously and are invested in quality care.
- Opportunities: Depending on employer needs and state requirements, certification may support advancement, broader responsibilities, and access to more roles.
DANB exams and credentials
Passing DANB exams can support credentialing pathways such as Certified Dental Assistant (CDA), Certified Orthodontic Assistant (COA), and Certified Preventive Functions Dental Assistant (CPFDA), depending on the credential and eligibility requirements.
DANB common and past names
The Dental Assisting National Board (DANB) has used several names over time, including:
1949–1977: National Association of Dental Examiners (NADE)
1977–1990: National Commission on Dental Assisting (NCDA)
1990–1998: Dental Assisting National Board
1998–present: Dental Assisting National Board, Inc. (DANB)
Technical Facts
DANB CDA Fast Facts
- Three component exams
- Computer-based, multiple-choice
- 245 questions total
- 195 minutes total
- 100–900 scaled scoring
- 400 to pass each
Exam structure
| Component exam | Questions | Time |
|---|---|---|
| General Chairside (GC) | 95 | 75 minutes |
| Radiation Health and Safety (RHS) | 75 | 60 minutes |
| Infection Control (ICE) | 75 | 60 minutes |
Other DANB certifications (overview)
| Certification | Exams required |
|---|---|
| NELDA | AMP, ICE, RHS |
| COA | OA, ICE |
| CPFDA | CP, SE, TF |
| CRFDA | IM, TMP, SE, RF |
| CDIPC | CDIPC |
| DISIPC | DISIPC |
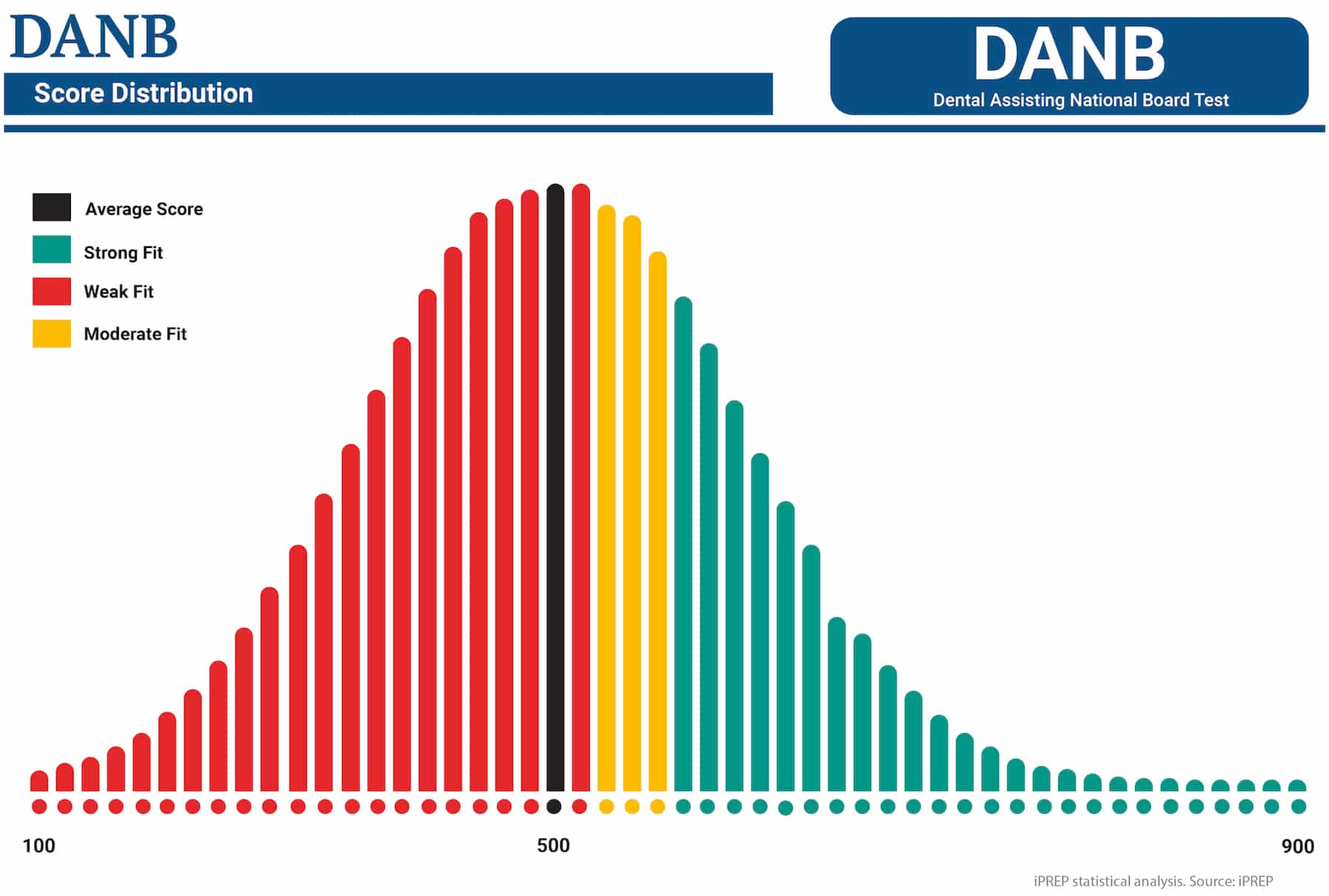
Results Scale and Interpretations
DANB result analysis
DANB reports exam performance using a scaled score. Scaled scores range from 100 to 900, and a score of 400 is required to pass each CDA component exam. Because the exam uses scaled scoring, your score is not a direct “percent correct” or “number correct,” and score reports may include performance feedback by content area.
When you get results
After you test, you are typically notified by email within 1–3 business days when your results are available in your online DANB account.
DANB result interpretation
A passing score indicates you met the exam’s minimum standard for knowledge-based competence. If you do not pass, you may retake the exam based on the applicable retest rules and fees.
DANB CDA Exam Eligibility Criteria
Eligibility for CDA depends on the pathway you qualify under and is confirmed during the application process. In general, candidates should expect to provide proof of education and/or work experience (as required for their pathway), meet any CPR/BLS requirements, submit supporting documentation, and complete the application and payment through DANB before scheduling an exam. State rules for dental assisting can differ, so confirm any additional state-specific requirements that apply to you.


FAQs
DANB offers nationally recognized dental assisting exams and credentials, including the National Entry Level Dental Assistant (NELDA), Certified Dental Assistant (CDA), Certified Orthodontic Assistant (COA), and Certified Preventive Functions Dental Assistant (CPFDA).
The CDA credential is earned by passing three component exams: General Chairside (GC), Radiation Health and Safety (RHS), and Infection Control (ICE).
Exam fees vary by exam and can change over time. Each component exam is paid separately, and the total cost depends on which exams you take and when you apply. Check your DANB account or the current DANB fee schedule for the latest pricing.
DANB uses a scaled score from 100 to 900. A scaled score of 400 is required to pass each CDA component exam. Score reports may also include performance feedback by content area.
Renewal requirements depend on the credential, but DANB certifications are commonly renewed on an annual cycle and may require continuing education, CPR/BLS status (as applicable), and a renewal fee.
Dental assisting duties and allowable functions vary by state. Check your state dental board’s rules and any state-specific summaries available through DANB resources.
DANB exams are delivered at secure Pearson VUE test centers. After you apply through DANB and your eligibility is approved, you’ll receive instructions to schedule your exam appointment.
Administration
Test administrator: Dental Assisting National Board (DANB)
Test schedule: After your application is approved, you have 60 days to schedule and take your exam. If needed, you may request one additional 60-day testing window.
Test format: Computer-based, multiple-choice. Exams can be taken at a secure test center, and some exams may be available with online proctoring.
Test materials: No notes or reference materials are allowed during testing. What you may bring into the room is limited and controlled by the testing provider; personal items are typically stored during the exam.
Cost: Fees vary by exam and can change. As a reference, the GC, RHS, and ICE exams are typically $270 each, and a CDA (GC+RHS+ICE in the same administration) application is typically $450.
Retake policy: CDA components are scored separately. If you don’t pass a component, you typically retake only the component(s) you didn’t pass by submitting a new application and fee, following the current retest rules.
Test Provider
The Dental Assisting National Board (DANB) administers dental assisting certification exams, including the CDA exams. DANB is widely recognized in the dental industry, and DANB credentials are commonly referenced by employers and state dental boards when reviewing qualifications and allowable duties. DANB also offers additional certifications beyond CDA, depending on role and eligibility.
Information Sources
Disclaimer – All information and preparation materials on iPREP are provided for educational and tutoring purposes only. iPREP is not affiliated with DANB, which owns and publishes the registered trademarks CDA, COA, NELDA, GC, ICE, RHS, and any other trademarks referenced on this page.
Free DANB practice test: Preview the Dental Assistant Certification exam experience by answering sample questions in a timed, exam-style format.
GC Sample Question 1 of 3
What is the purpose of a dental matrix?
- To cover the tooth and protect it from damage during a procedure.
- To create an impression of the tooth for a crown or bridge.
- To hold composite material in place while it is being cured.
- To remove calculus and plaque from the tooth surface.
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
A dental matrix is a thin, flexible strip that is placed around a tooth to hold composite material in place while it is being cured. This helps to create a tight contact between the filling material and the tooth, which prevents food and bacteria from getting stuck between the tooth and the filling. Options A, B, and D are incorrect because they do not accurately describe the purpose of a dental matrix.
GC Sample Question 2 of 3
Which of the following filling materials is typically hardened using a blue curing light?
- Composite resin
- Glass ionomer
- Amalgam
- Gold
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
Composite resin restorations are commonly light-cured using a blue curing light to activate polymerization and harden the material.
Why the other answers are wrong:
D: Gold restorations are fabricated outside the mouth and cemented in place; they are not hardened with a curing light.
B: Glass ionomer typically sets through an acid–base reaction and is not primarily light-cured (some versions are resin-modified, but standard glass ionomer does not require a curing light).
C: Amalgam hardens through a chemical reaction and does not require a curing light.
GC Sample Question 3 of 3
What is the primary function of dental sealants?
- To restore a decayed tooth
- To whiten discolored teeth
- To protect teeth from decay
- To replace missing teeth
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
Dental sealants are a thin coating that is applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth to protect them from decay. They work by filling in the grooves and pits of the teeth, creating a smooth surface that is easier to clean and less likely to trap food particles and bacteria.
RHS Sample Question 1 of 3
What is the maximum permissible dose (MPD) of radiation exposure for occupational workers in the United States?
- 5 millisieverts (mSv) per year.
- 10 millisieverts (mSv) per year.
- 50 millisieverts (mSv) per year.
- 100 millisieverts (mSv) per year.
The correct answer is C.
Explanation:
The maximum permissible dose (MPD) of radiation exposure for occupational workers in the United States is 50 millisieverts (mSv) per year. This limit is set by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) and is designed to protect workers from the harmful effects of radiation exposure. Options A, B, and D are incorrect because they do not accurately describe the MPD for radiation exposure in the United States.
RHS Sample Question 2 of 3
Which change reduces the patient’s radiation dose the most during intraoral dental radiographs?
- Using rectangular collimation instead of round collimation
- Increasing exposure time
- Decreasing the distance between the X-ray source and the patient
- Using a slower image receptor
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
Rectangular collimation limits the X-ray beam to the size of the image receptor, reducing exposed tissue area and significantly lowering patient dose.
Why the other answers are wrong:
D: A slower receptor typically requires more exposure, increasing dose.
B: Increasing exposure time increases the amount of radiation.
C: Decreasing distance increases exposure due to the inverse square law.
RHS Sample Question 3 of 3
What is the purpose of the collimator on a dental x-ray machine?
- To produce a high-quality image
- To control the size and shape of the x-ray beam
- To protect the patient from radiation exposure
- To prevent artifacts on the radiograph
The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
The collimator is a device on the x-ray machine that controls the size and shape of the x-ray beam. It helps to limit the amount of radiation exposure to the patient by ensuring that only the area of interest is exposed to radiation. This also helps to produce a high-quality image by reducing scatter radiation and minimizing artifacts on the radiograph.
ICE Sample Question 1 of 3
Which of the following is an example of a critical item that must be sterilized before use?
- Protective eyewear
- Dental chair
- Amalgamator
- Scalpel blade
The correct answer is D.
Explanation:
Critical items penetrate soft tissue or bone and must be sterilized (or be single-use sterile) to prevent infection transmission. A scalpel blade is a critical item.
Why the other answers are wrong:
C: An amalgamator is noncritical and is cleaned/disinfected as needed; it does not penetrate tissue.
A: Protective eyewear is noncritical and is cleaned and disinfected, not sterilized.
B: The dental chair is noncritical and is cleaned/disinfected between patients.
ICE Sample Question 2 of 3
Which of the following sequences is the correct order for donning PPE for patient care?
- Hand hygiene → gloves → mask → gown
- Hand hygiene → gown → mask/respirator → eye protection → gloves
- Gown → gloves → hand hygiene → mask
- Mask → gown → gloves → hand hygiene
The correct answer is B
Explanation:
A standard donning sequence starts with hand hygiene, then gown, followed by mask/respirator, eye protection, and gloves to reduce contamination risk.
Why the other answers are wrong:
D: Hand hygiene is not performed after donning gloves as part of the donning sequence.
A: Gloves should be put on last, after mask and eye protection.
C: Hand hygiene should be performed before putting on PPE, and gloves are not put on before the mask.
ICE Sample Question 3 of 3
Which of the following is an example of a critical item in a dental office?
- Blood pressure cuff
- Dental explorer
- Exam gloves
- Sterilization pouches
The correct answer is B.
Explanation:
Critical items are used to penetrate soft tissue or contact bone and must be sterilized. A dental explorer is used intraorally and is processed as a sterilized instrument between patients.
Why the other answers are wrong:
D: Sterilization pouches are packaging materials; they are not instruments used to penetrate tissue.
A: A blood pressure cuff is noncritical and is cleaned/disinfected.
C: Exam gloves are single-use disposable items and are not reprocessed.